Introduction
Collagen supplements have become part of the daily diet for many people – whether to support skin, connective tissue or joints.
But the question often arises: Is there an ideal time to take it?
Why the timing can be interesting
From the mid-twenties onwards, the body gradually produces less collagen .
Therefore, the intake of hydrolyzed collagen peptides can be a useful addition to a normal diet.
Whether in the morning, after training or in the evening: The choice of time can depend on individual goals.
Possible times for taking it
1. In the morning – For an active start
Many people prefer to take collagen on an empty stomach , as this could make absorption in the small intestine particularly efficient.
Conveniently, collagen can be stirred into coffee, tea or smoothies without leaving a taste .
2. Before or after training – support for muscles and joints
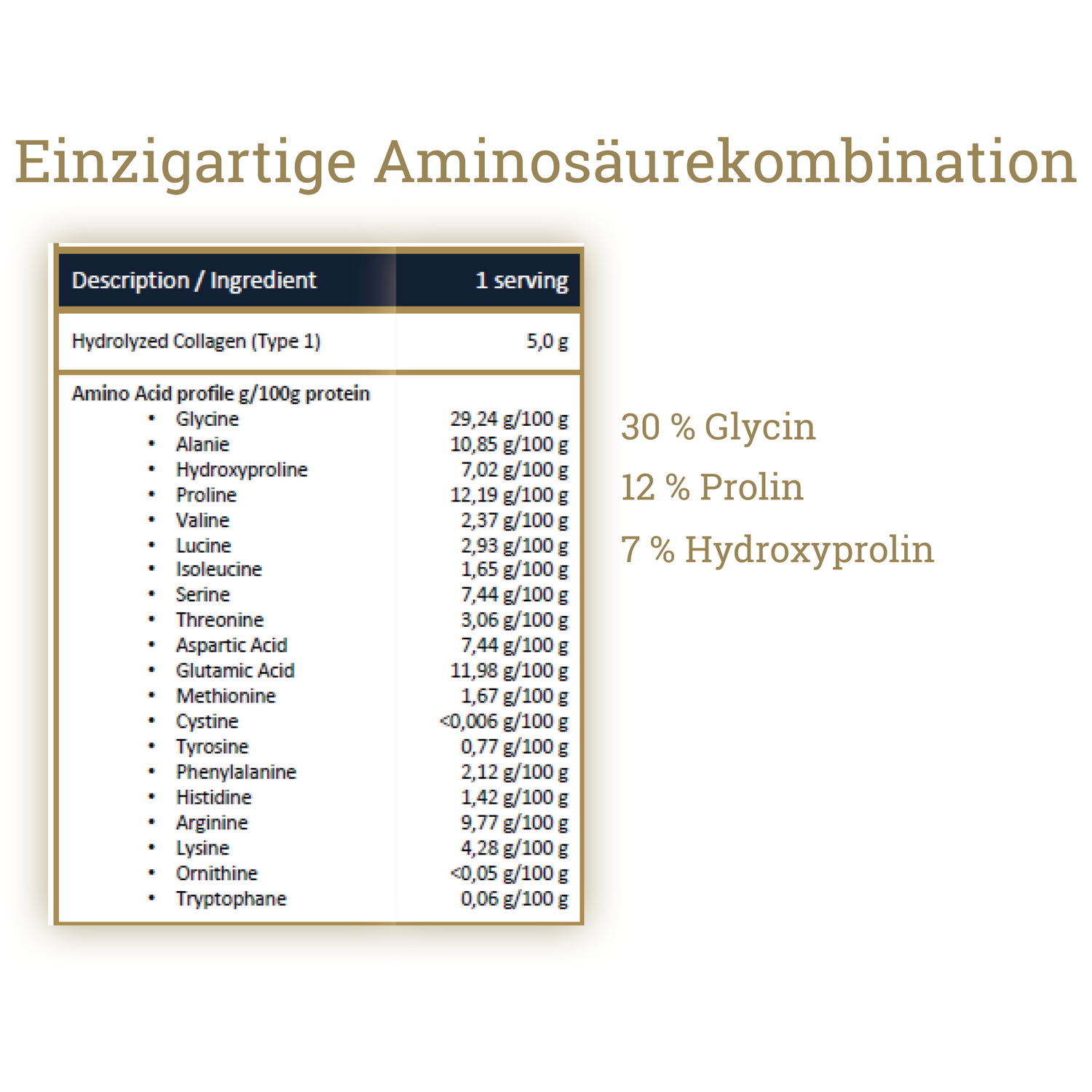
Collagen provides amino acids such as glycine and proline, which are important for connective tissue.
Taking it 30–60 minutes before or after exercise is well suited to phases in which the body is particularly active in regenerating.
3. In the evening – to accompany nighttime regeneration
Many building and repair processes take place in the body during sleep.
Taking it in the evening may therefore be of interest to people who want to specifically support skin and connective tissue structures .
Scientific background to the recording
Studies show that hydrolyzed collagen can be detected in the blood within about one to two hours .
This means that the body can utilize collagen flexibly , regardless of the time of day.
Marine collagen peptides – readily available and high quality
Marine collagen, for example from Norwegian salmon , has a high bioavailability due to its small molecular size .
It contains predominantly type I collagen , which occurs naturally in skin, bones and connective tissue.
Conclusion
There is no single "right" time to take collagen.
What's more important is regularity – whether in the morning, after training, or in the evening.
Who Choosing high-quality salmon collagen offers the benefit of good absorption and allows for flexible intake to fit into one's daily routine.
Sources
-
Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry (2014): Intake of hydrolyzed collagen
-
British Journal of Nutrition (2019): Collagen peptides in combination with training
-
EFSA Journal: Assessment of collagen hydrolysate as a food ingredient