An overview of omega-3 fatty acids and their nutritional importance

Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fatty acids and are considered essential nutrients – this means that the body cannot produce them itself and they must be obtained through food.
They are found particularly in fatty cold-water fish and high-quality omega-3 oils. Scientific studies have repeatedly investigated links between the intake of certain omega-3 fatty acids and various physiological functions—for example, heart function, brain function, and vision.*
In this guide, we'll give you a clear overview: What are the different types of omega-3 fatty acids? How do they differ? And what should you look for when choosing an omega-3 product?
Whether you are new to the topic or would like to supplement your diet with Omega-3, you will find comprehensive information about it here.
Table of contents
- What are omega-3 fatty acids?
- What do the abbreviations EPA and DHA mean?
- Possible functions of EPA and DHA in the human body
- Which foods contain omega-3 fatty acids?
- Why the ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 in the diet is important
- What amounts of omega-3 fatty acids are considered recommended?
- What should you consider when taking Omega-3 during pregnancy?
- Omega-3 fatty acids and child development – what do studies show?
- Omega-3 in connection with bone and joint metabolism – what is known?
- What role could omega-3 fatty acids play for muscles?
- DHA and the maintenance of normal vision – scientific evidence
- Contribution of DHA and EPA to normal heart function – according to approved health claim
- Skin care through nutrition – what role does Omega-3 play?
- Is there evidence of a link between omega-3 intake and mental well-being?
- What are the possible side effects of taking Omega-3?
- What makes Norwegian fish oil special?
- What should you look for when choosing an Omega-3 product?
- What distinguishes Ballstad Omega-3 from other products?
What are Omega-3 fatty acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fatty acids and are essential for the human body because they cannot be produced naturally. They are found in foods such as fatty fish (e.g., salmon, herring), certain vegetable oils, and nuts and seeds. Omega-3 supplements are also available, allowing for targeted intake—especially when the body isn't getting enough of them through its daily diet.
A frequently asked question concerns the difference between omega-3 and fish oil: Fish oil is a source of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, especially EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), which, in certain amounts, can contribute to the normal function of the heart, brain, and eyes.*
Both women and men can benefit from a needs-based supply of omega-3 fatty acids – for example, as part of a balanced diet and a health-conscious lifestyle. Dietary supplements can support this if individual needs are not met through diet.
What do the abbreviations EPA and DHA mean?
EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) are long-chain omega-3 fatty acids found primarily in fatty marine fish and fish oil. With sufficient daily intake, they contribute to the normal function of the heart, brain, and eyes.
EPA is particularly known for its role in the formation of certain tissue hormones (eicosanoids), while DHA is an essential structural component of nerve cells and the retina.
Since the human body can only produce EPA and DHA to a very limited extent, fatty sea fish and fish oil products are considered suitable sources. Dietary supplements containing EPA and DHA are often used when adequate intake is not provided through diet. Individual requirements can vary depending on lifestyle and diet.
Possible functions of EPA and DHA in the human body
EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) are long-chain omega-3 fatty acids found primarily in fatty marine fish and fish oil. The human body can only produce these fatty acids to a very limited extent, which is why adequate intake through diet or supplementation can be beneficial.
EPA and DHA contribute to the normal function of the heart with a total daily intake of 250 mg.
When taken in sufficient quantities, DHA contributes to the maintenance of normal vision and brain function.
During pregnancy, DHA contributes to the normal development of the brain and eyes in the fetus and breastfed infant (with a daily intake of 200 mg in addition to the recommended intake of 250 mg EPA+DHA).
In addition, DHA is a natural component of nerve cells and the retina. EPA is linked in the scientific literature to the regulation of certain endogenous signaling molecules.
To support a balanced diet, professional associations recommend the regular consumption of oily sea fish. If this isn't possible, the use of high-quality dietary supplements can be an alternative.
Which foods contain omega-3 fatty acids?
The most important dietary sources of the marine omega-3 fatty acids EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) include fatty marine fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and tuna. For people who rarely or never eat fish, fish oil supplements may be a suitable addition to their daily diet.
Plant sources such as flaxseed, chia seeds, walnuts, and algae provide the short-chain omega-3 fatty acid ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). The human body can only convert ALA into EPA and DHA to a limited extent, so a direct intake of EPA and DHA via fish or corresponding supplements is considered more efficient.
The ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 fatty acids is also important for a balanced diet. Omega-6 fatty acids, which are primarily found in vegetable oils and highly processed foods, should be in a balanced ratio with omega-3 fatty acids. A sufficient supply of omega-3 fatty acids helps maintain this ratio.
Why is the ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 important in the diet?
Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fatty acids that the body needs for various functions. While both types of fatty acids are important, excessive consumption of omega-6 fatty acids—as is common in many Western diets—can lead to an imbalanced fatty acid pattern.
A balanced ratio of these fatty acids contributes to a sufficient supply. Vegetable oils and processed foods generally contain large amounts of omega-6. At the same time, the intake of marine omega-3 fatty acids—especially EPA and DHA—is often considered too low.
Fatty marine fish or high-quality fish oil supplements directly supply EPA and DHA. These two fatty acids are recognized in certain areas of life, such as maintaining normal heart function, normal blood pressure, or normal blood triglyceride levels – but only in conjunction with a defined daily intake according to the approved EU health claims.
Anyone who wants to determine their individual needs or check their omega-3 intake can do so, for example, with an Omega-3 Index test. This allows them to specifically supplement and better balance their personal diet.
What amounts of omega-3 fatty acids are considered recommended?
The recommended intake of omega-3 fatty acids—especially EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid)—can vary depending on life stage and individual needs. A general recommendation is often around 250–500 mg of EPA and DHA daily, as recommended by European health authorities, for example, to maintain certain bodily functions.
In special life situations, a higher intake may be useful:
During pregnancy and breastfeeding
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) recognizes that, in addition to the normal intake of EPA and DHA, a daily supplement of 200 mg DHA for pregnant and breastfeeding women contributes to the normal development of the brain and eyes in the fetus and breastfed infant.
For active sports enthusiasts
During training phases, increased intake can be part of an individually tailored nutrition plan. Studies in this context are investigating, among other things, the influence of certain fatty acids on the recovery process and subjective well-being after physical exertion.
Eyes & Vision
DHA contributes to the maintenance of normal vision – with a daily intake of 250 mg DHA.
Heart & Vessels
EPA and DHA together contribute to the maintenance of normal heart function at a daily intake of 250 mg. Higher doses are being investigated in some studies; in such cases, use should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
Individual nutritional situation
Those who eat little oily fish can meet their needs with selected supplements. To reliably assess their intake, an Omega-3 Index test is recommended. This measures the levels of EPA and DHA in red blood cells.
What should you consider when taking Omega-3 during pregnancy?
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) – a long-chain omega-3 fatty acid – has been shown to contribute to the normal development of the brain and eyes in the fetus and breastfed infant.* Therefore, a targeted intake of DHA during pregnancy and breastfeeding may be beneficial.
Since DHA is primarily found in fatty sea fish, pregnant women are advised to ensure they get an adequate supply through their diet or selected supplements. It's important to choose products of certified purity—e.g., purified fish oil that has been tested for contaminants.
DHA remains a relevant nutrient even during the postpartum period and during breastfeeding: It contributes to normal brain function – a property that, according to EFSA, can be attributed to a daily intake of 250 mg DHA.*
A notice:
The selection and dosage of dietary supplements should be individually coordinated with a doctor – especially during sensitive phases of life such as pregnancy and breastfeeding.

Omega-3 fatty acids and child development – what do studies show?
The omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) contributes to normal brain development and vision in children.* DHA plays a particularly important role in growth because it is a natural component of brain cells and the retina.
Regular intake of DHA through your diet—e.g., through fatty seafood—can help meet your needs. If this isn't possible, selected dietary supplements can be a complementary option. It's important to pay attention to quality and purity.
The recommended daily intake for children varies by age, but according to professional organizations, it is usually between 200 and 500 mg of DHA. A medical professional should be consulted for the exact dosage.
Omega-3 in connection with bone and joint metabolism – what is known?
Omega-3 fatty acids, especially EPA and DHA, are polyunsaturated fatty acids known to contribute to the maintenance of normal body functions. They are often mentioned in connection with a balanced diet—even by people who value their mobility and joint function.
EPA and DHA contribute to normal heart function.* Furthermore, their role in a varied and balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle is being investigated. This raises questions about whether these fatty acids can provide support for certain everyday complaints, such as limited mobility. However, strict legal requirements apply to health claims related to joints. For this reason, dietary supplements are currently not permitted to claim efficacy for the relief of joint pain or inflammatory diseases.
Anyone wishing to supplement their omega-3 fatty acids with high-quality fish oil products should pay attention to purity and certified quality. If in doubt, consult a medical professional.
What role could omega-3 fatty acids play for muscles?
Omega-3 fatty acids, especially EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), are polyunsaturated fatty acids and are an important component of a balanced diet – even for physically active individuals. They are a component of cell membranes and are being studied in the context of various physiological processes.
Many physically active individuals consciously incorporate EPA and DHA into their diet, for example, by consuming fatty sea fish or fish oil products. The goal is often to support a balanced diet, especially during periods of intense physical exertion.
Several scientific studies have examined the possible connections between omega-3 fatty acid intake and processes such as muscle recovery or exercise tolerance. While specific health claims regarding muscle function or recovery cannot currently be made in connection with dietary supplements, there is evidence that EPA and DHA can be part of a healthy lifestyle for physically active individuals.
For consumers who wish to supplement their diet in a targeted manner, it is advisable to pay attention to the quality and purity of fish oil products and to consult medical professionals if they have any individual questions.
DHA and the maintenance of normal vision – scientific evidence
Omega-3 fatty acids, especially DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), are a natural component of the retina and are being studied in nutritional research in relation to various aspects of vision.
There is growing interest in the potential influence of omega-3 fatty acids on subjective eye well-being, such as dryness. DHA and EPA—found in fish and fish oil—are particularly in focus, as they are polyunsaturated fatty acids and can be included in a balanced diet.
Scientific studies are investigating whether there is a connection between the intake of these fatty acids and factors such as tear film stability or age-related changes in vision. Specific health claims are currently not permitted by law, but there is evidence that some people find an omega-3-rich diet beneficial.
Anyone looking to supplement their diet with specific nutrients should pay attention to the origin and quality of the products. If you have any specific complaints or questions about eye health, we recommend consulting a medical professional.
Contribution of DHA and EPA to normal heart function
Omega-3 fatty acids such as EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) are polyunsaturated fatty acids found in fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines. They are being studied in nutritional research in connection with various aspects of cardiovascular function.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has approved health claims for EPA and DHA: A daily consumption of 250 mg of EPA and DHA contributes to normal heart function.* In addition, DHA is involved in maintaining normal brain function and vision.*
Some studies suggest that regular intake of EPA and DHA may be associated with certain parameters such as triglyceride levels, blood pressure, or endothelial function. These findings are currently undergoing further scientific investigation and may not be generalized or promoted without an approved health claim.
Anyone interested in fish oil supplements should pay attention to transparent ingredient declarations, controlled origin, and the dosage of omega-3 fatty acids. In addition to a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle, a targeted intake of EPA and DHA can be beneficial. If you have existing medical conditions or are unsure about the product, we recommend consulting a medical professional.
* The effect occurs with a daily intake of 250 mg EPA and DHA.
Skin care through nutrition – what role does Omega-3 play?
Omega-3 fatty acids such as EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), which are particularly found in fish oil, are polyunsaturated fatty acids. These nutrients are components of cell membranes and contribute to their structural integrity. Studies are currently investigating their connection to skin functions.
A balanced diet with omega-3 fatty acids has been linked to several factors, including skin barrier function and moisture levels. Current scientific evidence suggests that adequate omega-3 fatty acid intake may be important for individuals with an imbalanced fatty acid profile.
Numerous studies are also investigating the potential influence of EPA in the context of oxidative stress and light-induced skin changes. Inflammatory skin processes such as eczema or skin redness are the focus of scientific studies – especially in clinical contexts. However, under current law, statements about specific efficacy may only be made with demonstrably approved health claims.
A balanced diet with sources of marine omega-3 fatty acids can contribute to your daily intake of these nutrients. Dietary supplements can be an additional option, especially if your fish intake is low. Those who want to focus on their skin health should ideally consult with a medical or nutritionist.
Is there evidence of a link between omega-3 intake and mental well-being?
The importance of polyunsaturated fatty acids for general health has been scientifically investigated for many years – particularly in relation to cognitive functions and emotional well-being. In this context, the marine omega-3 fatty acids EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) are the focus of numerous studies.
Scientific publications suggest that adequate dietary intake of EPA and DHA is associated with various neurobiological processes—including brain signaling and inflammation-related mechanisms associated with the central nervous system. These relationships are currently being intensively researched, particularly with regard to psychological stress or mood changes.
Some studies address the question of whether an adjusted intake of EPA can complement conventional therapeutic approaches—for example, in adults experiencing increased emotional stress. However, such scientific findings are context- and population-dependent, which is why medical advice is generally recommended for specific complaints.
The importance of DHA and EPA during pregnancy and breastfeeding is also well documented, particularly with regard to the development of the child's brain. Adequate intake during this phase of life is subject to nutritional recommendations and can be individually coordinated with medical professionals.
Whether through fatty seafood or certified dietary supplements, anyone looking to increase their omega-3 intake should pay attention to guaranteed quality and transparent origins. Dietary supplements are not a substitute for therapy, but, in consultation with a physician, can play a supportive role in a balanced lifestyle.
What are the possible side effects of taking Omega-3?
Omega-3 fatty acids are among the polyunsaturated fatty acids that are scientifically studied in relation to various bodily functions, including cardiovascular processes, cognitive functions and aspects of general well-being.
At the recommended dosage, omega-3 supplements—such as fish oil capsules with EPA and DHA—are generally well tolerated by healthy adults. As with many fatty foods, sensitive individuals may experience mild gastrointestinal intolerance, especially when taking higher doses.
In isolated cases, an altered tendency to blood clotting has been observed with very high intakes. Such effects are particularly relevant when the recommended daily intake is exceeded over a long period of time. Therefore, it is advisable to adhere to the manufacturer's recommended intake and to seek medical advice beforehand if you have underlying medical conditions or are taking blood-thinning medications.
High-quality fish oil supplements are characterized by careful purification, transparent origins, and standardized levels of EPA and DHA. Those who want to supplement their diet with omega-3 should look for certified quality and incorporate the product into a balanced lifestyle.

What should you look for when choosing an Omega-3 product?
Fish oil supplements from Norway are known worldwide for their high quality and purity. Production takes place under the supervision of the Norwegian Food Safety Authority (NFSA), which is known for its particularly strict requirements for product safety, environmental compatibility, and consumer protection. These standards ensure a high level of control and transparency throughout the entire production chain.
Norwegian manufacturers use modern processing methods to preserve the natural properties of fish oil to the best of their ability. Undesirable residues are removed without unnecessarily compromising the nutritional content, contributing to a pure and well-tolerated end product.
The production facilities in Norway operate with advanced technologies and strict quality controls. Many consumers appreciate this level of care—especially when choosing dietary supplements produced under controlled conditions.
If you are looking for fish oil supplements that are produced under strict legal requirements and that stand for a responsible manufacturing process, Norwegian fish oil is a reliable choice.
What should you look for when choosing an Omega-3 product?
Choosing a suitable omega-3 supplement should be done carefully. When making your decision, pay attention to the origin of the raw materials – high-quality fish oil often comes from cold-water fish and is produced under controlled conditions. Products from Norway, in particular, are known for their careful processing and quality standards.
The ratio of EPA to DHA can be considered depending on individual needs. While EPA is preferred in certain contexts, combined preparations containing EPA and DHA are widely available. The composition should be transparently labeled.
The degree of freshness also plays a role in determining reliable quality. Products with low TOTOX values (a measure of oxidation) are considered particularly fresh and neutral in flavor. This information can help you assess whether an oil has been well processed.
The form of the supplement is also important: capsules, oils, or vegan algae-based alternatives – choose the option that suits your lifestyle. A combination of a balanced diet and a supplement can be beneficial to support your supply of omega-3 fatty acids.
What distinguishes Ballstad Omega-3 from other products?
Ballstad Omega-3 is a high-quality dietary supplement with carefully processed fish oil, valued for its purity, freshness, and careful sourcing. Manufactured in Norway under strict quality standards, Ballstad stands for transparency and uncompromising raw material selection.
Each batch is carefully processed and checked for freshness. Modern processes are used to help preserve the oil's natural character. The result: a concentrated fish oil with high levels of EPA and DHA – two valuable omega-3 fatty acids.
Ballstad also sets standards in terms of sustainability: The fish oil comes from responsibly managed stocks and is extracted in compliance with ecological standards.
Ballstad Omega-3 is characterized by particularly low TOTOX values (a measure of the freshness and stability of fish oil) – an indicator of careful production and good tolerability.
The small capsules are easy to swallow and can be easily integrated into your daily routine. Just three capsules a day allow you to supplement your diet in a targeted manner – without any unpleasant taste.
Ballstad stands for quality, traceability and the conscious use of natural resources – for all those who value origin, purity and reliability in their nutritional supplements.













Fresh Omega-3 Fish Oil Capsules - 1 Month
- Regular price
-
€54,90 - Regular price
-
€0,00 - Sale price
-
€54,90 - Unit price
-
€752,05 per kg
Share with your friends
























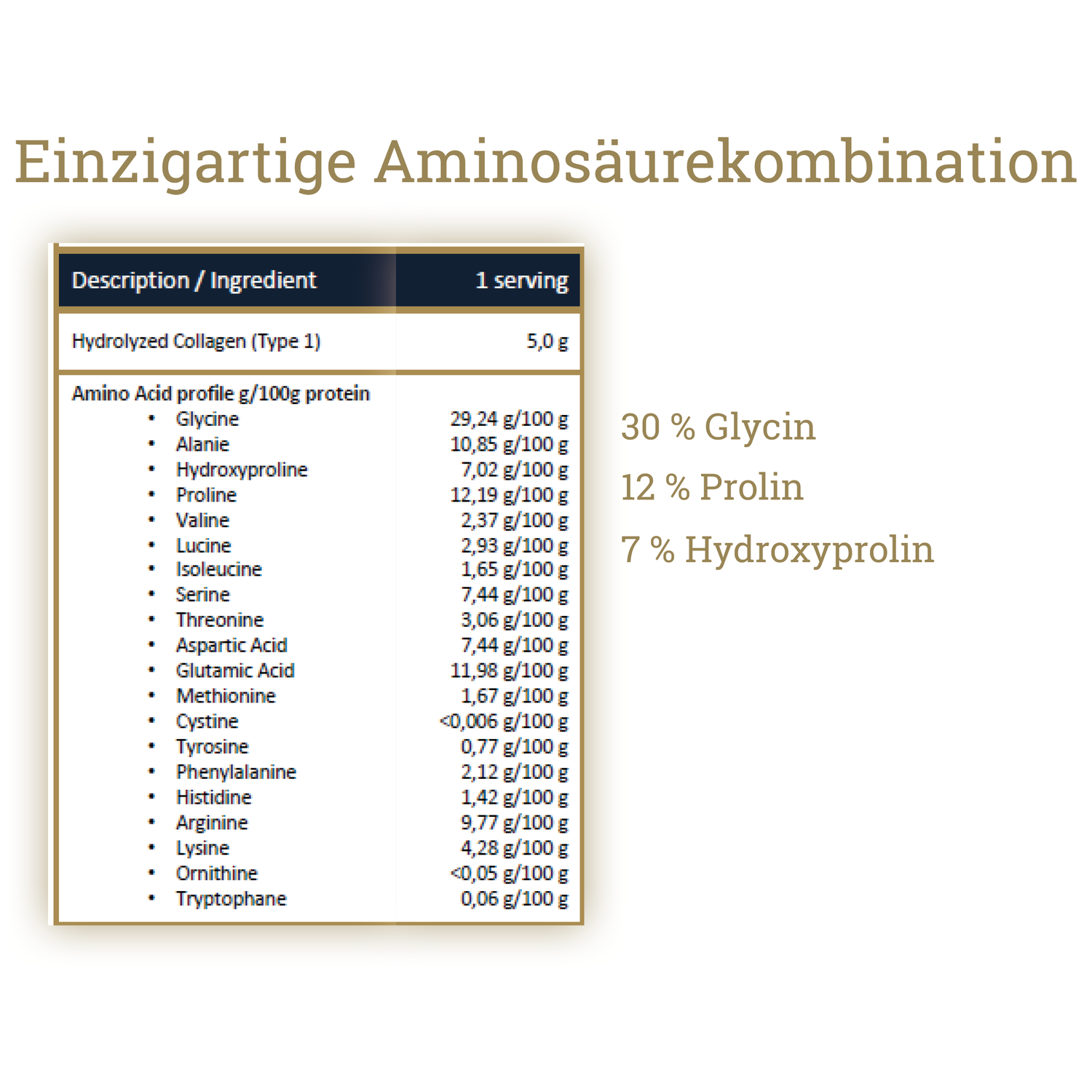
Salmon collagen - 1 month
- Regular price
-
€109,90 - Regular price
-
- Sale price
-
€109,90 - Unit price
-
€686,88 per kg
Share with your friends














