Understanding Collagen: Its Function in the Body and Its Importance

Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body – it plays a key role in skin, joints, bones, and connective tissue. However, with age, the body's own collagen production naturally declines. This is a normal part of the aging process and can affect, among other things, skin structure and tissue resilience.
Many people are therefore interested in collagen supplements as a complement to a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle. In this guide, you'll learn what collagen actually is, the different forms it comes in, and how you can meaningfully integrate it into your daily routine.
Table of contents
- What is collagen?
- The different types of collagen (type I, II, III, etc.)
- How collagen works in the body
- Natural collagen production and why it decreases
- The importance of collagen for skin, hair and nails
- The role of collagen in joints and bones
- Collagen and muscle strength: A look at the research
- Does collagen have an impact on gut health?
- Collagen during pregnancy and breastfeeding
- The connection between collagen and aging processes
- Food sources of collagen: What to look out for
- Collagen supplements: powder, capsules or liquid forms
- How much collagen per day is beneficial?
- When is the best time to take collagen?
- Can collagen improve sleep and regeneration?
- Are there any possible side effects from taking collagen?
- Salmon collagen compared to bovine or porcine collagen
- Choosing a high-quality collagen supplement
- What makes Ballstad Collagen special?
What is collagen?
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body, accounting for approximately 30% of total protein content. It acts as a structural building block and contributes to the stability and resilience of skin, joints, bones, tendons, and connective tissue. It is often described as a kind of "glue" that holds the body together.
As we age, the body's collagen production naturally declines—this typically begins around the age of 25. This process is one of the normal changes associated with aging and can affect, among other things, skin and tissue structure.
Many people are therefore interested in collagen supplements, for example in the form of hydrolyzed fish collagen peptides. These are popular because of their special processing.
Whether it's for skin, joints, or general well-being, anyone who studies collagen first gains a better understanding of its role in the body. Choosing a high-quality source is crucial to ensure a sensible addition to a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle.
The different types of collagen (type I, II, III, etc.)
There are many different types of collagen in the human body, but the most common forms used in supplements are type I, type II, and type III. Each type has a specific role, and understanding their differences can help in choosing the right supplement.
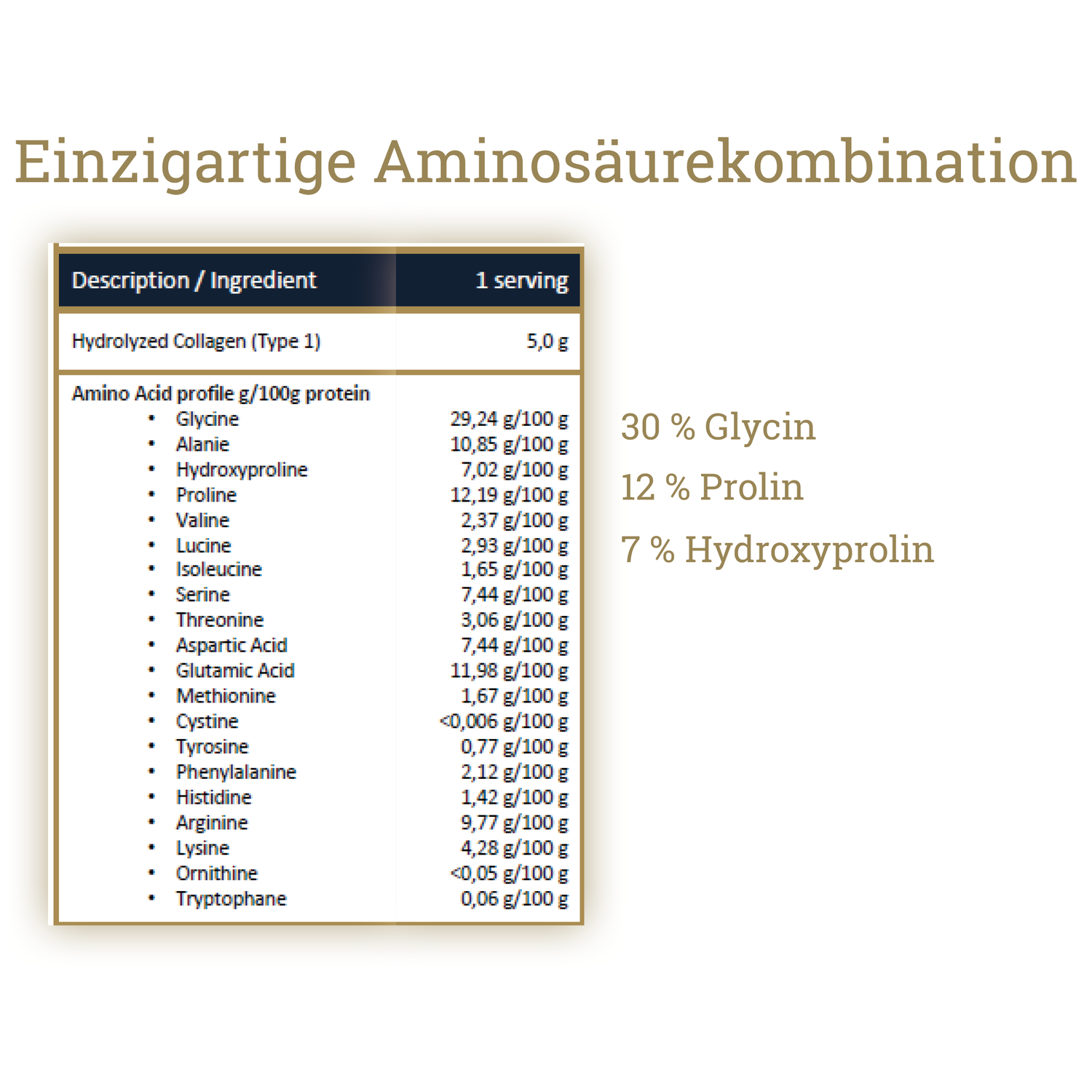
Type I collagen is the most widespread form. It is found primarily in skin, bones, tendons, ligaments, and connective tissue. Type I is also the main component in most marine collagen supplements.
Type II collagen is found in cartilage tissue and is important for the structure and resilience of joints. It is less common in fish collagen and is more often used in products specifically formulated for joint health.
Type III collagen often occurs together with type I, for example in skin, blood vessels and internal organs. It contributes to the tissue structure in these areas.
Other collagen types, such as type V and type X, fulfill specific functions, but together types I, II and III make up over 90% of the body's own collagen.
Salmon collagen, such as Ballstad collagen, is naturally rich in type I collagen. Because of this property, it is particularly valued when it comes to high-quality collagen supplements.
How collagen works in the body
Collagen is an important structural protein that contributes to the stability, elasticity, and strength of tissue. It is produced by cells called fibroblasts, which combine amino acids such as glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline into collagen fibers. These fibers form a network that provides structure to skin, joints, bones, tendons, and connective tissue.
In the skin, collagen plays a role in strength and structure. In joints and cartilage, it contributes to resilience, while in bone tissue and tendons, it supports stability. Collagen is also an important component in blood vessels and other tissue structures.
As we age, the body's own collagen production slows down. This is part of the normal aging process and can be further influenced by external factors such as UV radiation or an unbalanced diet.
Many people therefore turn to hydrolyzed collagen, such as fish collagen. Due to its special processing, it is in a form that is easily absorbed by the body. Such preparations are used as a supplement to a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle.
Natural collagen production and why it decreases
Collagen is produced in the body by cells called fibroblasts. These cells use amino acids such as glycine and proline, as well as vitamin C, to produce collagen fibers. These fibers give skin, bones, tendons, and connective tissue their structure and strength. The body's own collagen production is particularly active during a young age.
However, from around the age of 25, natural collagen production gradually declines – on average by about 1–1.5% per year. This process is a normal part of aging. Additionally, external influences such as UV radiation, smoking, stress, high sugar consumption, or an unbalanced diet can exacerbate this process.
Over time, these changes can affect the skin, joints, bones, and other tissue structures. Many people are therefore interested in collagen supplements—especially hydrolyzed fish collagen. Due to its special processing, it is in a form that is easily absorbed by the body. Such products are often chosen as a supplement to a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle.
(Note: Vitamin C has been shown to contribute to normal collagen formation for the normal function of skin, bones, cartilage, teeth, gums, and blood vessels.)
Importance of collagen for skin, hair and nails
Collagen is an essential structural protein for skin, hair, and nails. In the skin, it helps build connective tissue in the dermis, thus ensuring structure and firmness. Natural collagen production decreases with age – this is a normal part of bodily changes.
Collagen also plays a role in hair follicles and nails as a component of tissue structure. Changes in the body's own production can therefore affect their stability.
Many people are interested in collagen supplements, especially in the form of hydrolyzed fish collagen peptides. Thanks to a special processing method, these are in a form that is easily absorbed by the body. Such products are often chosen as a supplement to a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle.
Research is currently investigating the relationship between collagen intake and skin and tissue structure. In this context, salmon collagen is particularly valued due to its high proportion of type I collagen – the type that is also most common in the human body.
The role of collagen for joints and bones
Collagen is a key structural protein essential for the stability of joints and bones. It forms a major component of cartilage tissue, which covers the joint surfaces and thus contributes to resilience and mobility. With increasing age, the body's own collagen production decreases – this is a normal part of the aging process and can affect tissue structure.
Collagen also plays a crucial role in bones, as it forms the basic framework into which minerals such as calcium are deposited. In this way, it contributes to the strength of the bone matrix.
Many people are therefore interested in collagen supplements, such as hydrolyzed salmon collagen peptides. Thanks to a special processing method, these are in a form that is easily absorbed. Such products are often chosen as a supplement to a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle.
Salmon collagen is rich in type I collagen, the most common form found in the human body. This makes it attractive to many consumers who want to specifically supplement their diet with regard to joint and bone health.
Collagen and Muscle Strength: A Look at the Research
Collagen is often associated with skin and joints, but it's also increasingly attracting research attention in relation to muscle structure. It contains high levels of glycine and proline—amino acids that are important components of muscle and connective tissue. Although collagen isn't a complete protein, many people use it as a supplement in combination with regular exercise.
A 2015 study published in the British Journal of Nutrition examined older men who took collagen peptides alongside resistance training. This study showed differences in muscle parameters compared to a control group. Such results suggest that the relationship between collagen intake and muscle structure represents an interesting area of research.
Fish-based collagen, such as Ballstad Collagen, is characterized by its special processing and good bioavailability. Many users therefore value it as part of a balanced diet combined with exercise and a healthy lifestyle.

Does collagen affect intestinal health?
Collagen is also gaining increasing importance with regard to the digestive system. The amino acids contained in collagen – including glycine, proline, and glutamine – are important building blocks of proteins that perform a variety of functions in the body.
A balanced protein profile contributes to the supply of nutrients to the body's cells, including those lining the digestive system. For this reason, collagen is valued by many people as a supplementary protein source.
Salmon collagen is considered to be particularly well-digested (hydrolyzed) and therefore easily absorbed. It is frequently chosen by people who want to supplement their diet with a high-quality collagen source – as part of a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle.
Collagen during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Collagen is a key structural protein that stabilizes skin, joints, and connective tissue. During pregnancy, the body undergoes significant changes that place increased stress on these tissues. Because collagen is rich in amino acids such as glycine and proline, it is valued by many as a supplementary protein source.
Even after childbirth, collagen remains an important component of the body, as skin, muscles, and connective tissue continue to be subjected to stress. Some women are interested in collagen supplements during this phase as an addition to a balanced diet.
Salmon collagen, such as hydrolyzed fish collagen peptides, is considered particularly well-digested and easily absorbed. As part of a varied diet and a healthy lifestyle, it can provide an additional way to supply the body with protein building blocks during this special phase of life.
(Note: Dietary supplements should always be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding after consulting a doctor.)
The connection between collagen and aging processes
Collagen plays a central role in the structure of skin, joints, and bones. Starting in the mid-20s, the body's own collagen production begins to gradually decline—a process that becomes more pronounced with age. This decline is a normal part of aging and can affect the condition of skin and connective tissue, as well as the stability of bones.
Additionally, external influences such as sun exposure, smoking, stress, or an unbalanced diet can impair collagen fibers. Over the years, this can contribute to changes in skin and tissue structure.
Many people are therefore interested in hydrolyzed collagen, for example, from marine sources such as Ballstad Collagen. Thanks to its special processing, it is available in a form that is easily absorbed. Such products are often chosen as a supplement to a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle.
Food sources of collagen: What to look out for
Collagen is naturally present in various animal-based foods, particularly in connective tissue, bones, and skin. Bone broth, made by simmering bones and connective tissue for an extended period, is one of the richest sources. Chicken skin, fish skin, pigskin, and beef tendons also contain structural proteins similar to human collagen. Fish with skin on additionally provides valuable omega-3 fatty acids.
Besides foods that directly contain collagen, other nutrients also play a role in the body's own collagen production. These include:
Vitamin C (e.g. in oranges, kiwis, strawberries) → contributes to normal collagen formation for the normal function of skin, bones, cartilage, teeth, gums and blood vessels.
Zinc (e.g. in seafood, eggs, seeds) → contributes to normal protein synthesis.
Copper (e.g. in nuts, offal) → contributes to the maintenance of normal connective tissue.
Since the collagen content in foods can vary greatly, many people also opt for dietary supplements – especially in the form of hydrolyzed salmon collagen. These can be used as part of a varied diet and a healthy lifestyle.
Collagen supplements: powder, capsules or liquid forms
Collagen supplements are available in various forms—powder, capsules, or liquid products. Which option is best often depends on personal preference and the desired level of comfort.
Powder is considered particularly versatile because it can be easily stirred into beverages like coffee or smoothies. Many users also appreciate its neutral taste and flexible dosage.
Capsules are convenient for on the go or while traveling. Since the amounts per capsule are usually smaller, taking several capsules per day may be necessary.
Liquid products are often offered as a ready-to-drink alternative. However, depending on the manufacturer, they contain additional ingredients such as flavorings or sweeteners that may not be to everyone's taste.
Ultimately, all forms have their advantages. Many people choose powder because it's easy to integrate into everyday life. The key is choosing a high-quality product that fits your diet and lifestyle.
How much collagen is useful per day
The amounts of hydrolyzed collagen peptides used in scientific studies typically range between 2.5 and 10 grams per day. The specific amount chosen depends on factors such as personal goals and diet.
Studies show that different dosages have been investigated in various fields of application – lower amounts from around 2.5 g as well as higher amounts around 10 g daily. Regular, long-term intake as part of a balanced diet is particularly important.
Salmon collagen is considered easily digestible due to its special processing method (hydrolysis). Many users therefore choose this source because it is rich in type I collagen – the most common form found in the human body.
Additionally, the intake of certain nutrients may be beneficial:
Vitamin C contributes to normal collagen formation for the normal function of skin, bones, cartilage, teeth, gums and blood vessels (EFSA Health Claim).
The best time to take collagen
There's no universally "perfect" time to take collagen supplements. More important than the time is regular use. Many people take collagen in the morning—perhaps in their coffee, smoothie, or with breakfast—while others prefer to incorporate it in the evening or around exercise. The key is to fit the intake into your daily routine and be consistent.
Regardless of the timing, combining it with vitamin C can be beneficial. Vitamin C has been shown to contribute to normal collagen formation for the normal function of skin, bones, cartilage, teeth, gums, and blood vessels (EFSA Health Claim).
Whether as powder or capsules, high-quality, hydrolyzed collagen supplements, especially from marine sources, can be used flexibly. The best time to take them is when they can be easily and permanently integrated into your individual diet and lifestyle.
Collagen, sleep and regeneration: Current findings
Collagen contains various amino acids, including glycine, which is considered interesting in research in relation to sleep and recovery. Some studies are investigating whether certain amino acids can influence well-being in the evening.
Furthermore, collagen is valued by many people as a supplementary protein source due to its amino acid profile, especially in the context of athletic activity. In this context, it is often used as part of a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle.
Salmon collagen, which is present in hydrolyzed form, is considered particularly bioavailable. Some people prefer to incorporate it into their evening routine, as it can be easily combined with other dietary habits.
Are there any possible side effects when taking collagen?
Collagen supplements are generally considered well-tolerated when used in recommended amounts. Studies with hydrolyzed collagen peptides—regardless of whether they come from beef, pork, or fish—show that side effects are rare. Some people report mild digestive discomfort such as a feeling of fullness or bloating when they first start taking them, especially with higher amounts.
Allergic reactions are very rare, but can occur—especially when products contain additives or potential allergens. Therefore, it's advisable to pay attention to clean production, high-quality raw materials, and transparent origins. Ballstad Collagen, derived from salmon, is free of common allergens, synthetic fillers, and artificial additives—and is therefore valued by many users.
To avoid adverse reactions, dosage recommendations should always be followed. People who are pregnant, breastfeeding, or have special dietary requirements should always seek medical advice before taking the medication.

Salmon collagen compared to bovine or porcine collagen
Salmon collagen has become a popular alternative to bovine or porcine collagen in recent years. It is primarily derived from the skin and scales of fish and is naturally rich in type I collagen – the most common form in the human body, found mainly in skin, bones, and connective tissue.
Another advantage of marine collagen lies in its special processing: Through the hydrolysis process, it is broken down into smaller peptides that can be easily utilized by the body.
Furthermore, salmon collagen is considered a clean and sustainable choice. Compared to some animal sources, it is free from agricultural additives such as hormones or antibiotics and is also suitable for people who avoid beef or pork for dietary or religious reasons.
Ballstad salmon collagen stands for purity, quality, and sustainable sourcing. Many consumers appreciate it as a supplement to a varied diet and a conscious lifestyle.
Choosing a high-quality collagen supplement
With such a wide selection of products available, finding the right collagen supplement can be challenging. A key criterion is the origin of the collagen. Supplements containing hydrolyzed collagen peptides are recommended, as these are broken down into smaller units through a special processing method, making them easily absorbed by the body. Salmon collagen is often valued for its purity and sustainable harvesting.
Transparency regarding ingredients is equally important. A high-quality collagen product should be free of unnecessary fillers, artificial additives, and known allergens. Ideally, it is tested for residues such as heavy metals and manufactured under strict quality standards. Independent third-party testing (e.g., laboratory tests) can provide additional assurance.
The type of collagen can also play a role in the choice: Type I and III are particularly common in the human body, while type II is mainly found in cartilage.
Furthermore, the amounts used in scientific studies can serve as a guideline: These typically involve dosages between 2.5 and 10 grams of collagen peptides per day. Consistent daily intake is important, regardless of the chosen form (powder or capsules).
Ultimately, it is worthwhile to rely on brands that stand for clean raw materials, transparent production and tested quality.
What makes Ballstad Collagen special
Salmon collagen stands out from many other products on the market due to its purity, sustainable sourcing, and high quality standards. Derived from salmon caught in pristine marine waters, Ballstad delivers naturally derived collagen peptides rich in type I collagen – the most abundant form of collagen in the human body. Through hydrolysis, the collagen is broken down into smaller peptides that are readily absorbed by the body.
A key focus of Ballstad products is their pure formulation: free from additives, artificial flavorings, and known allergens – making them suitable for people with sensitive dietary needs. Each batch undergoes rigorous testing, including checks for heavy metals and environmental residues. This Norwegian origin is reflected in the transparency, traceability, and strong commitment to quality.
For easy integration into everyday life, Ballstad Salmon Collagen is available both as an easily soluble powder and in convenient sticks. This allows it to be flexibly stirred into drinks such as coffee, tea, smoothies or water – completely without any aftertaste.
Ballstad Collagen combines sustainability, quality, and practicality, making it a popular choice for those who want to consciously supplement their diet. Ballstad Salmon Collagen stands out from many other products on the market due to its purity, sustainable sourcing, and high quality standards. Derived from salmon caught in pristine marine waters, Ballstad delivers naturally derived collagen peptides rich in Type I collagen – the most abundant form of collagen in the human body. Through hydrolysis, the collagen is broken down into smaller peptides that are easily absorbed by the body.
A key focus of Ballstad products is their pure formulation: free from additives, artificial flavorings, and known allergens – making them suitable for people with sensitive dietary needs. Each batch undergoes rigorous testing, including checks for heavy metals and environmental residues. This Norwegian origin is reflected in the transparency, traceability, and strong commitment to quality.
For easy integration into everyday life, Ballstad Salmon Collagen is available both as an easily soluble powder and in convenient sticks. This allows it to be flexibly stirred into drinks such as coffee, tea, smoothies or water – completely without any aftertaste.
Ballstad salmon collagen combines sustainability, quality and everyday usability, making it a popular choice for anyone who wants to consciously supplement their diet.









Salmon collagen - 1 month
- Regular price
-
€109,90 - Regular price
-
- Sale price
-
€109,90 - Unit price
-
€686,88 per kg
Share with your friends



























Fresh Omega-3 Fish Oil Capsules - 1 Month
- Regular price
-
€54,90 - Regular price
-
€0,00 - Sale price
-
€54,90 - Unit price
-
€752,05 per kg
Share with your friends















