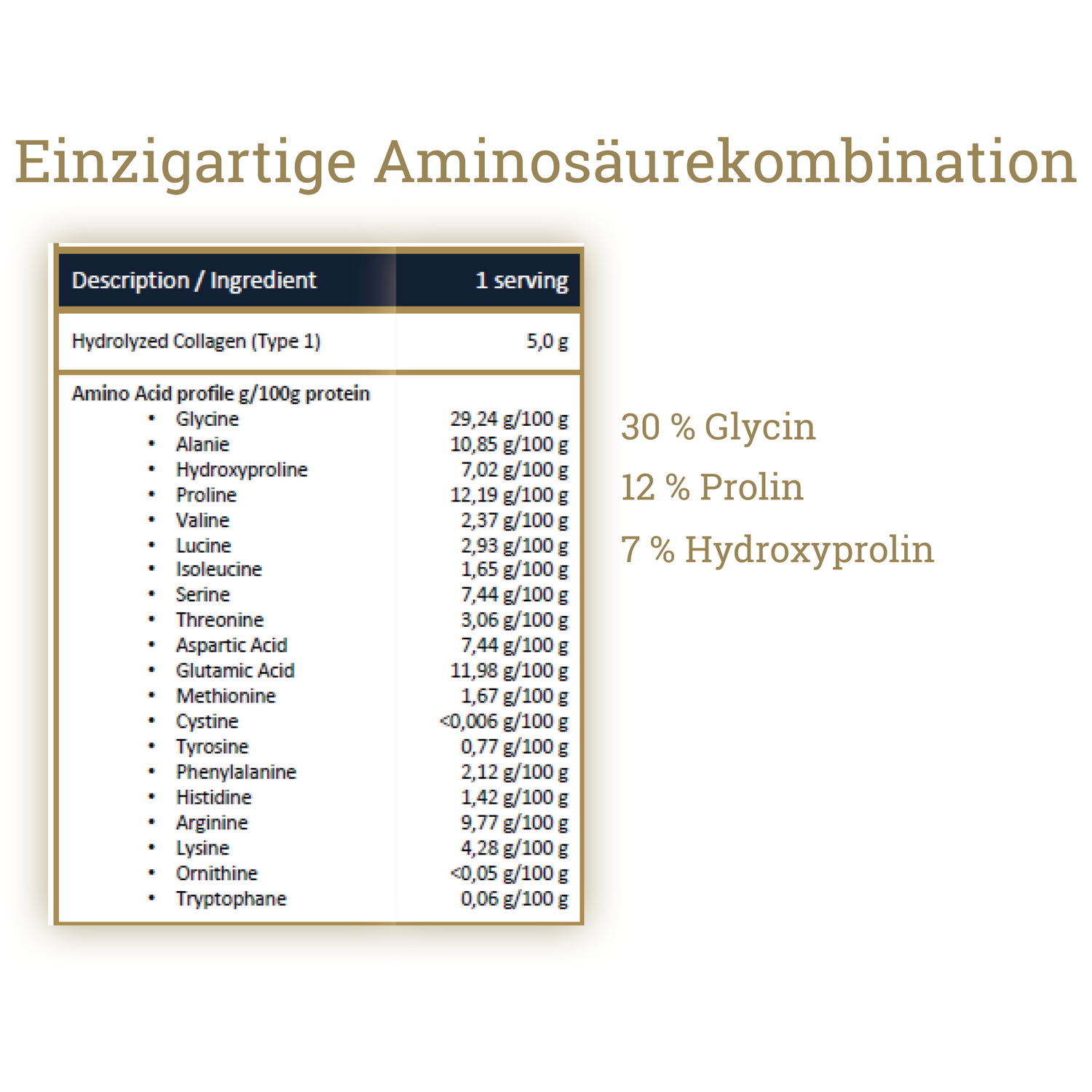
When we talk about collagen, many people think of smooth skin, flexible joints, or strong hair. But the structure of collagen contains another exciting building block that deserves more attention: glutamine . This amino acid performs numerous functions in the body – and those who consume collagen automatically absorb glutamine.
What is glutamine and why is it interesting?
Glutamine is an amino acid, a component of protein, and the most abundant amino acid in the human body. It is required for many basic metabolic processes—for example, for the construction of body tissue or as an energy source for certain cells.
Glutamine is naturally found in collagen
Hydrolyzed collagen—collagen broken down into peptides—provides glutamine in addition to glycine and proline. Regularly mixing high-quality collagen powder into smoothies or drinks automatically supplies the body with this amino acid without the need for a special glutamine supplement.
Versatile functions in the body
Glutamine is used, among other things, as fuel for cells in the digestive system, supports normal protein metabolism, and plays a role in recovery after physical exertion. The need for amino acids can increase, especially during periods of increased stress, such as during sports or intense physical activity.
Collagen as a practical source
While collagen isn't a pure glutamine supplement, it offers a versatile combination of various amino acids. Fish collagen—for example, from sustainably sourced salmon—is considered highly soluble and tasteless, making it easy to integrate into everyday life.
Conclusion
Glutamine may not be the star of the collagen world, but it's a quiet player with significance. Those who already incorporate collagen into their diet automatically benefit from its natural amino acid profile—glutamine included.
Note: This text is for general information purposes only and does not replace medical advice. For individual questions or specific dietary needs, always consult a doctor or qualified nutritionist.