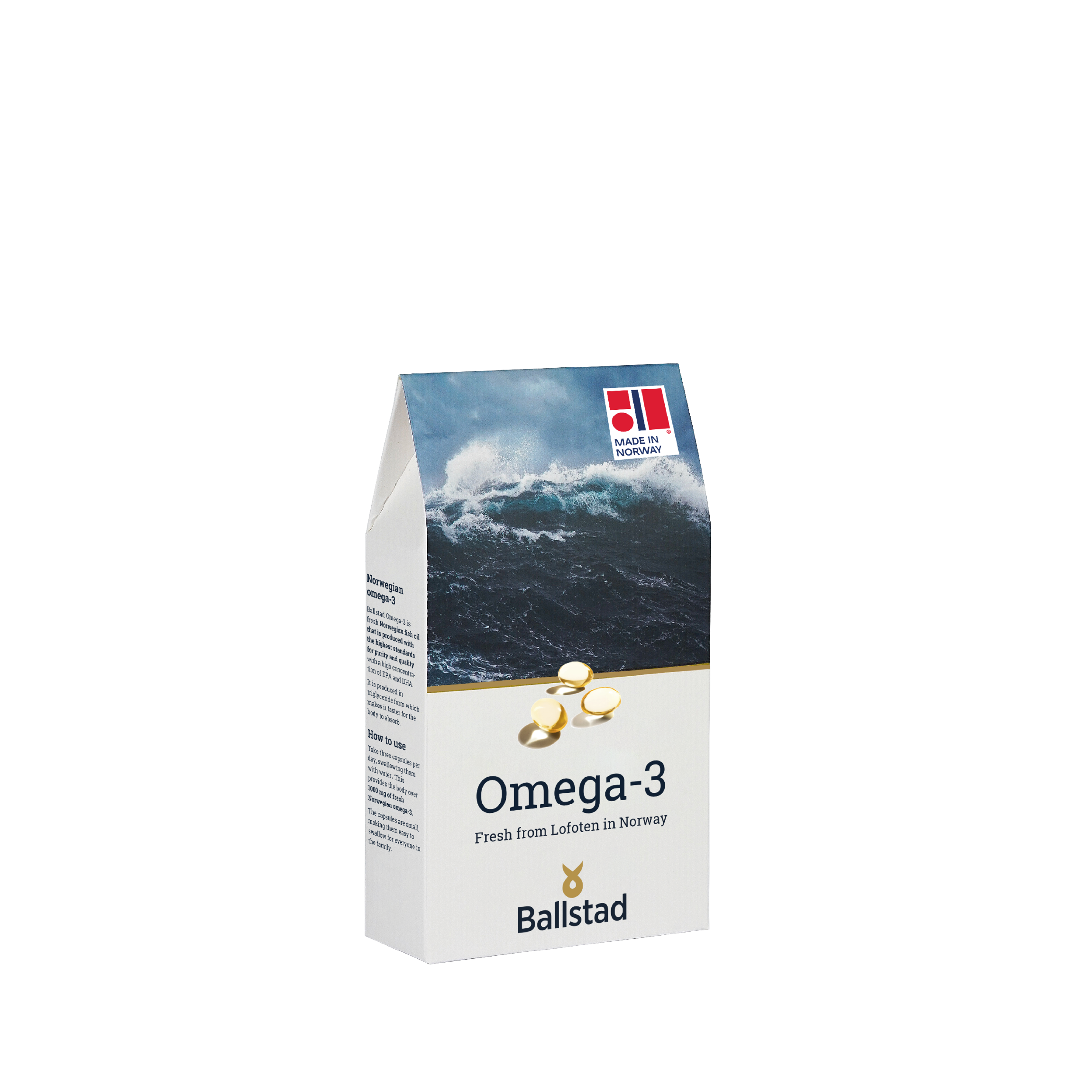
When we think of mobility and stability, muscles usually come to mind. But another, often overlooked system works in the background: our connective tissue. It forms the supporting structure for joints, tendons, and ligaments – and collagen is a key component of these tissues.
What belongs to connective tissue
Connective tissue is like an internal framework. This includes tendons, ligaments, cartilage, fascia, and the deeper layers of skin.
-
connect muscles to bones (tendons)
-
hold bones together (ligaments)
-
provide cushioning and mobility (cartilage)
-
support and shape the body (fascia)
Without stable connective tissue, everyday movements such as walking, stretching or sitting upright would hardly be possible.
The role of collagen
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body. It gives connective tissue strength, shape, and elasticity. With age, the body's own production of collagen declines—a normal part of the biological process.
Nutrition and possible supplements
A balanced diet provides building blocks such as protein, vitamin C, zinc and copper, which the body needs for natural collagen production.
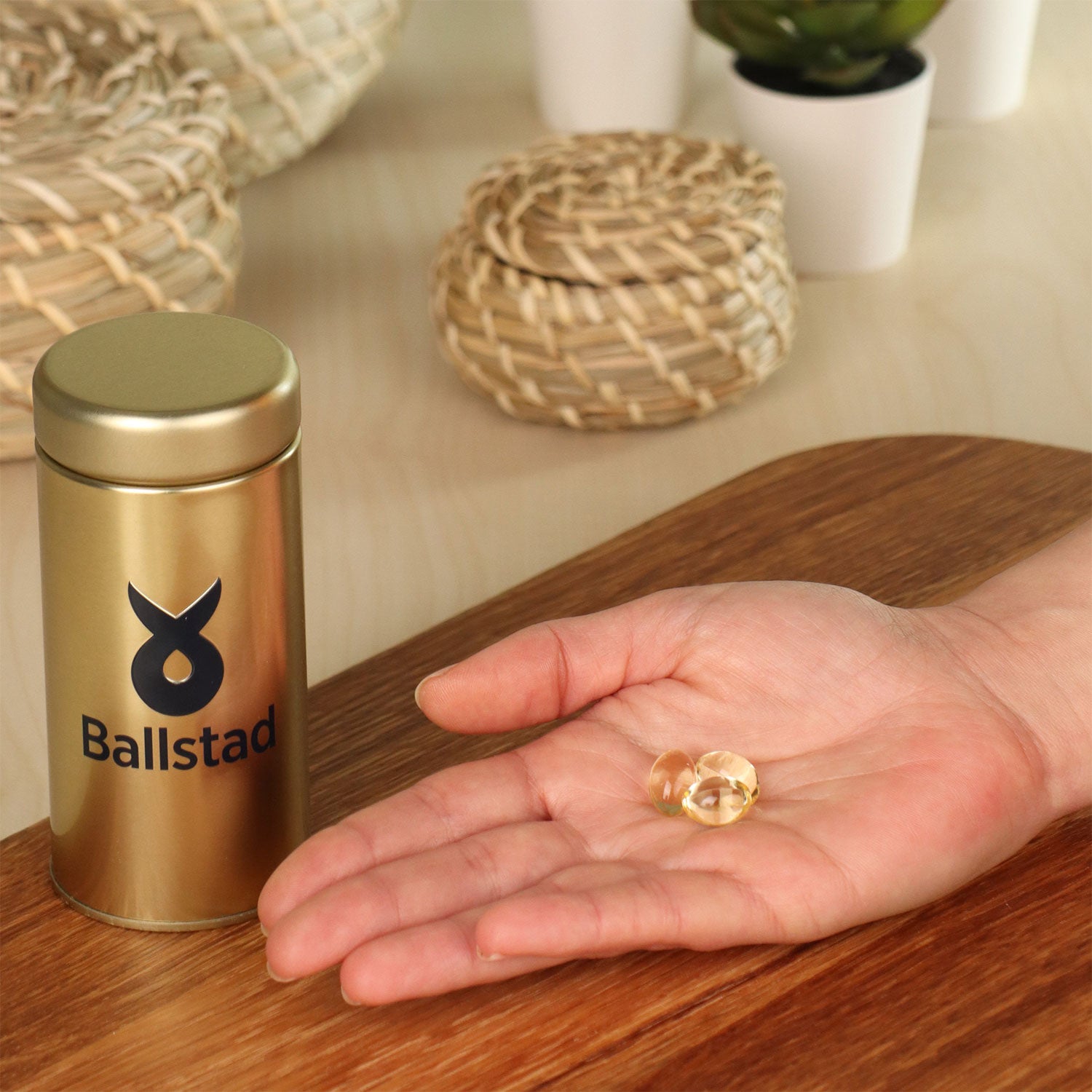
When choosing a dietary supplement, ideally, it's important to pay attention to its origin, quality, and purity. Products made from marine collagen (e.g., from fish) are known for their fine molecular structure and can be easily mixed into drinks or food.
Everyday tips for strong connective tissue
-
Regular exercise: Targeted strength and mobility training can adapt and strengthen tendons and ligaments.
-
Adequate regeneration: Rest and sleep support the natural maintenance of tissue structures.
-
Nutrient-rich foods: Fruits, vegetables, nuts and legumes provide important vitamins and minerals.
A notice:
This content is for general information purposes only and does not replace medical advice . It does not contain any claims of healing or health benefits within the meaning of the EU Health Claims Regulation (Regulation (EC) No. 1924/2006).