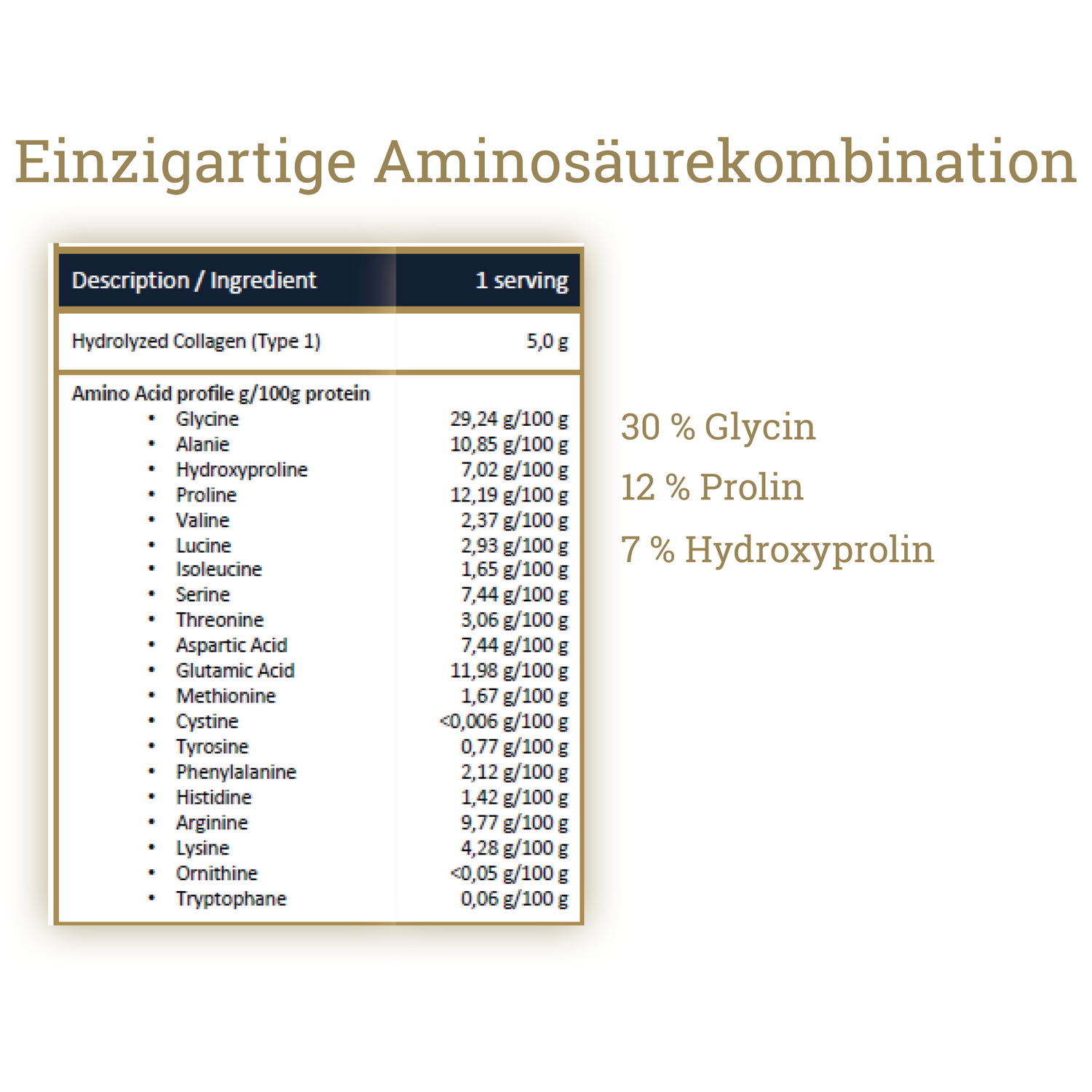
An overview of collagen in the body
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human organism.
It forms the structural framework for skin, bones, muscles and connective tissue .
Among the many known forms , types I , II and III are of particular importance.
If you know the differences, you can make a more targeted decision when choosing a collagen supplement.
Type I collagen – the basis for skin and bones
Type I makes up about 90% of all collagen in the body.
It is found primarily in skin, tendons, ligaments and bones and provides structure and strength .
Scientific studies show that collagen peptides can contribute to the maintenance of normal skin and connective tissue structures .
Bone tissue also depends on a stable collagen framework, which serves as the basis for mineralization.
Marine collagen , especially from fish, is rich in type I and is characterized by high bioavailability – meaning it is well absorbed.
Ballstad Salmon Collagen provides Type I collagen in a pure, tasteless form and can be easily stirred into drinks.
Type II collagen – important component of articular cartilage
Type II occurs predominantly in cartilage tissue .
It contributes to the elasticity and resilience of the joints and supports the normal function of the cartilage.
Studies are investigating the possible connection between type II collagen and the maintenance of healthy joint structures .
This makes preparations with type II interesting for anyone who wants to support their joint health .
Type III collagen – for connective tissue and vessels
Type III works closely with Type I.
It is found in skin, blood vessels, organs and muscles and contributes to tissue elasticity .
Collagen products that combine type I and type III can therefore support a holistic supply of connective tissue .
Choosing the right collagen supplement
When choosing a product, it is worth taking a look at the types included:
-
Type I – for skin, bones and general structure
-
Type II – for cartilage and joints
-
Type III – for connective tissue and vessels
Those seeking broad support can rely on preparations containing a combination of types I and III .
For targeted joint care, a product with type II is useful.
Ballstad Salmon Collagen offers sustainably sourced marine collagen with a high proportion of type I collagen – highly bioavailable and neutral in taste.
Sources
-
Ricard-Blum S. (2011): The Collagen Family – Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology
-
EFSA Journal: Evaluation of collagen hydrolysate and possible nutritional effects
-
BfR (Federal Institute for Risk Assessment): Information on collagen in food supplements
-
Regulation (EC) No. 1924/2006 on nutrition and health claims made on foods